Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cell micro RNA
4.5 (316) · $ 257.00 · In stock
HBdSMC miRNA is for research use only. It is not approved for human or animal use, or for application in in vitro diagnostic procedures.Quantity: 1 μg
Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cell microRNA (HBdSMC miRNA) is prepared from early passage Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells using Life Technologies' mirVanaTM miRNA Isolation Kit. The microRNA is purified by organic extraction and enriched by immobilization of RNA on glass-fiber filters. The microRNA is eluted and stored in nuclease-free water. MicroRNA from ScienCell Research Laboratories is a convenient and cost effective alternative to acquiring expensive tissues.

Growth properties of immortalized human bladder smooth muscle cells.

Differentiation of patient-specific void urine-derived human induced pluripotent stem cells to fibroblasts and skeletal muscle myocytes

PDF] Strain induced remodeling of urinary bladder smooth muscle
Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cell microRNA (HBdSMC miRNA) is prepared from early passage Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells using Life Technologies
Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cell MicroRNA

Calcium increase in immortalized human bladder smooth muscle cells. (A)

Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Initiates miRNA-mRNA Signaling Cascades in Obstruction-Induced Bladder Dysfunction - ScienceDirect
Isolated from human bladder tissue. HBdSMC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 105 cells in 1 ml volume.
Human Bladder Smooth Muscle Cells

Phenotypic modulation of human bladder smooth muscle cells. (A)
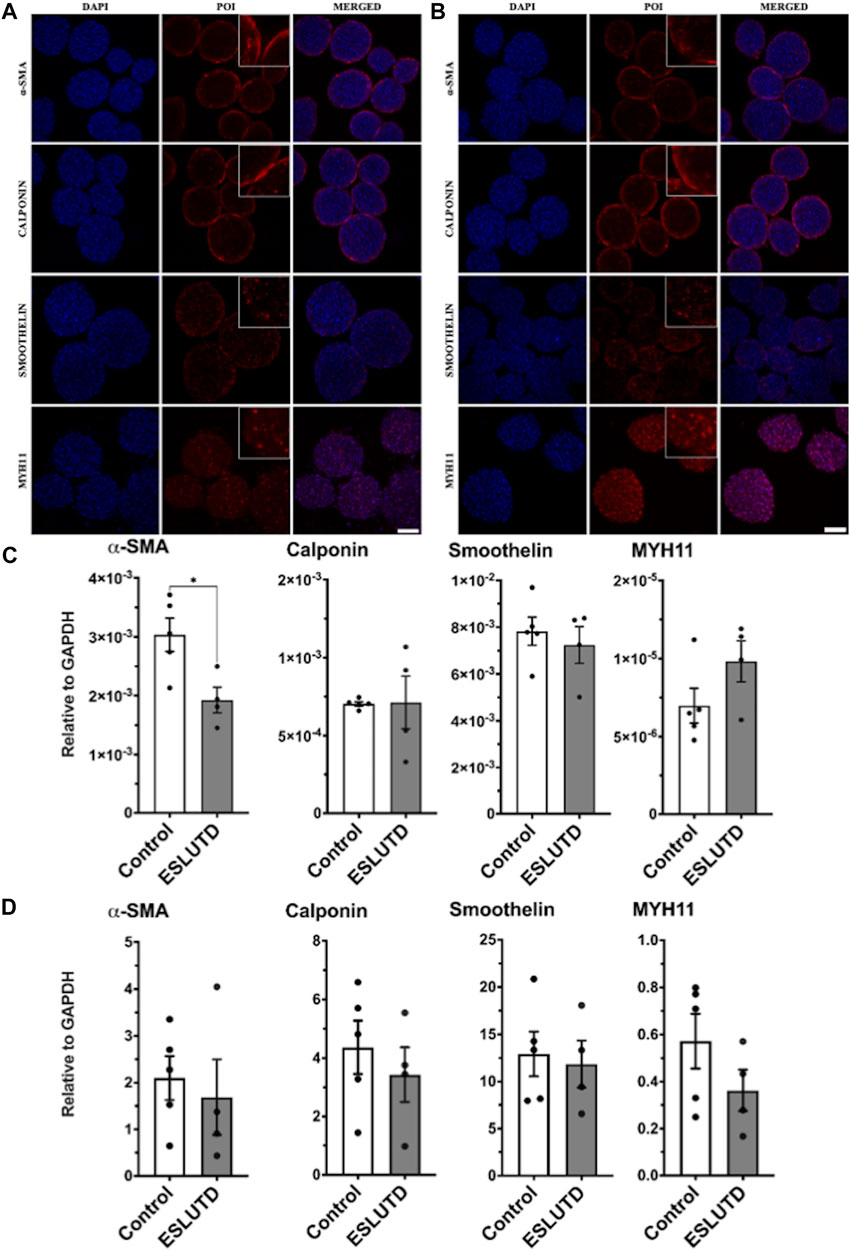
Frontiers Improved contractile potential in detrusor microtissues from pediatric patients with end stage lower urinary tract dysfunction

Mechanotransduction in gastrointestinal smooth muscle cells: role of mechanosensitive ion channels
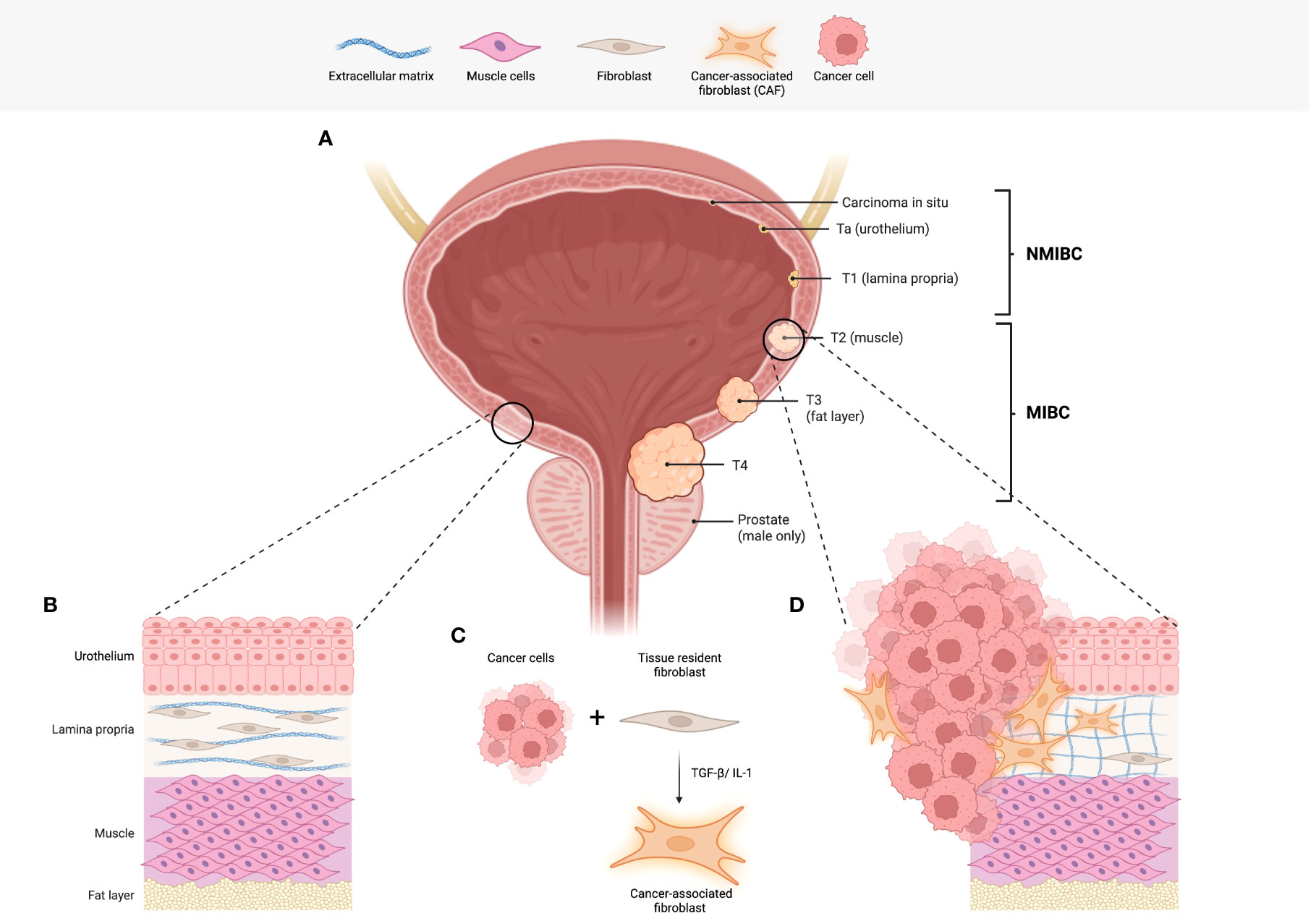
Frontiers A review of the biology and therapeutic implications of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in muscle-invasive bladder cancer

Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer - ScienceDirect